Health Articles
Find out more about your health here from our health professionals!

Constipation
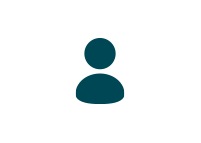
 Constipation is a very common problem people facing nowadays. Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard to pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful and stools hard to pass) and have a feeling that you have not fully emptied your bowels. Infrequent in this case means less than three times per week. Most of the time, constipation can be treated but if there is ongoing pain with bowel movements or there is blood in stool, seek medical assistance instead.
Constipation is a very common problem people facing nowadays. Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard to pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful and stools hard to pass) and have a feeling that you have not fully emptied your bowels. Infrequent in this case means less than three times per week. Most of the time, constipation can be treated but if there is ongoing pain with bowel movements or there is blood in stool, seek medical assistance instead.
What causes Constipation?
Common Lifestyle
- Eating foods low in fiber can make the stools become hard and difficult to pass.
- Changes in diet or daily routine especially when travelling along with inactivity
- Dehydration can worsen constipation, making the stool dry or like small lumps.
- Lack of exercise
- Often ignoring the urge to go to toilet due to too busy or doesn’t want to use the public toilet and as the feeling goes off , constipation occur
- Stress as when a person stressed, he/she is more likely to have an unhealthy diet, not getting enough exercise/sleep or forget to stay hydrated.
Medications and Health Condition
- Medicine like pain medications (mainly opioids), high calcium antacid and iron pills can cause constipation.
- Lazy Bowel Syndrome which the colon contracts poorly and restrains stool. ( due to excessive usage of stimulant laxative)
- Pregnancy

Treatment of Constipation
Lifestyle changes to treat constipation
Diet
- Eat a well-balanced diet with whole grains, fresh fruits and veggies. Aim for at least least 3 servings of vegetables and at least 2 servings of fruit per day. A serve is a portion equivalent in size of your own fist.
- Eat fewer high fat foods such as meat, eggs, cheese and processed foods.
- Add fiber supplements to your diet if needed. But remember to drink plenty of water because water help fiber work more efficiently.
- Drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Avoid caffeine-containing drinks and alcohol, which can cause dehydration.
Habit
- Don’t ignore the urge to pass motion. The longer you wait, the harder your stool can become.
- Check how you sit on the toilet. Raising your feet, leaning back or squatting may make having a bowel movement easier.
- Exercise regularly to prevent or treat constipation by lowering the time it takes for food to move through large intestine. Hence less water will be absorbed from the stool into body.
- Do not read, use your phone or other devices while trying to move your bowels.
Health Supplements
Probiotics
Probiotics can play a key role in helping to relieve constipation, but it can be confusing trying to choose the correct and most effective one. Here we aim to help you get the most out of your friendly bacteria.
Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus species are the majority bacteria found in our large intestine, hence probiotics with specific strains belonging to these species are regarded as the most suitable in helping to relieve constipation.
Megalive Floramax Pro, Megalive Flora 60 Plus, Bio-life A.B Junior Pre & Probiotics, Hexbio etc are probiotics supplements containing those strains which can be found in the market. Generally, probiotic food and supplements are thought to be safe for most people including during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist, choosing the most suitable probiotics for you and your family, turning unhappy tummies to happy ones.
Over-the-counter
There are a number of options to help treat constipation despite to the lifestyle changes. They can be found over-the-counter without a prescription and come in many forms like pills, powders (to mix with water), enemas or suppositories. Talk with your pharmacist to help you choose wisely.

Hemorrhoids
 Hemorrhoids also knows as piles that occur inside and around the anal passage. They are quite common to be happened. Hemorrhoids can either be internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids develop within the anus or rectum. External hemorrhoids develop outside of the anus. External hemorrhoids are the most common and most troublesome. Hemorrhoids cause pain, itching, bleeding and difficulty sitting. Fortunately, they are treatable.
Hemorrhoids also knows as piles that occur inside and around the anal passage. They are quite common to be happened. Hemorrhoids can either be internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids develop within the anus or rectum. External hemorrhoids develop outside of the anus. External hemorrhoids are the most common and most troublesome. Hemorrhoids cause pain, itching, bleeding and difficulty sitting. Fortunately, they are treatable.
Signs and Symptoms

Signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids usually depend on the types of hemorrhoids.
External hemorrhoids
These are under the skin around your anus. Signs and symptoms are:
– Itching and irritation in your anal region
– Pain or discomfort
– Swelling around your anus
– Bleeding
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids lie inside the rectum, which usually you can’t see or feel it. But straining or irritation when passing stool can cause:
– Painless bleeding, you might notice small amount of bright red blood on toilet tissue or in the toilet.
– A hemorrhoid to push through the anal opening ( prolapsed or protruding hemorrhoid), resulting in pain or irritation.
Causes
Hemorrhoids are usually caused by constipation. Constipation can make you to strain when you go to toilet so it puts pressure on the blood vessel in the anus which ca make them become swelling.
Other things can increase the risk of getting hemorrhoids are:
– Ageing
– Being obese
– Sitting for long periods of time on the toilet
– Regularly lifting heavy things
– Straining during bowel movement
– Having diarrhea or constipation
– Pregnancy
Complications
Anemia
It is rarely happen, but chronic blood loss from hemorrhoids may cause anemia.
Strangulated Hemorrhoid
If the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, then the hemorrhoid may be “strangulated,” which can cause extreme pain.
Blood Clot
Occasionally, a clot can form in a hemorrhoid which know as thrombosed hemorrhoid. Although it is not dangerous, but it can cause extremely painful.
Preventions
Eat high fiber foods
Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains. It can help in soften the stool that will help you avoid the straining which can cause hemorrhoids and pass the stool more easily.
Drink plenty of fluids
Drink six to eight glasses of water which can help you avoid constipation.
Don’t strain
Straining when you are trying to pass a stool creates greater pressure in the veins in the lower rectum which will cause hemorrhoids.
Obesity
Obesity is another factor of hemorrhoids, and you can lose your weight by exercising regularly, consuming low fat diet and reducing consumption alcohol intake.
Good Hygiene
Practice good hygiene by cleaning your anus with warm water during a shower or bath every day and keep your bottom clean and dry. But don’t use soap, as soap can aggravate hemorrhoids. Also avoid using dry or rough toilet paper when you wipe after a bowel movement.
Treatments
Fiber supplements
Most of people don’t get the enough fiber intake daily. And studies shown that over the counter fiber supplements such as psyllium or methylcellulose improved overall symptoms and bleeding from hemorrhoids.
But when you eat fiber supplement must be make drink enough of water daily. It can cause constipation if it does not.
Sitz bath
A sitz bath is referred to sitting a few inches of warm water 3 times a day for 15 to 20 minutes. A sitz bath may help in decrease the inflammation of hemorrhoids. Drying off the anal area completely after sitz bath which can minimize the moisture that can irritate the skin around your rectal area.
Medical procedures
If home treatments aren’t helping with your hemorrhoids, your doctor might recommend getting a rubber band ligation. This procedure involves the doctor cutting off circulation to the hemorrhoid by placing a rubber band around it.
This causes loss of circulation to the hemorrhoid, forcing it to shrink. This procedure should only be performed by a medical professional.

Importance Of Gut Microbiota In Nutrition And Human Health

What is Gut and Gut Micriobiota ?
Gut refers to the gastrointestinal or in simpler terms, the digestive system which starts from the mouth and ends at the rectum. It contains a number of microorganisms which are not visible to naked eye. Gut microbiota refers to all the microorganisms living in the same environment, while microbiome refers to all genes of these microbes. So, the gut microbiota refers to the large community of microbes that reside in the gut.
What is the function of Gut Microbiota ?
The gut microbiota plays an important role in digestion, absorption and metabolism of food. On the other hand, the gut bacteria are thought to play an important role in obesity, immune function and minimally responsible in influencing mood. In fact, our gut bacteria is said to have an impact on most of our physiological functions, directly or indirectly. While the research around the gut microbiota is still ongoing, it is clear that it is a key factor in several aspects of the body’s optimal functioning.
What are the common gut related disorders and why does it occur ?
In certain situations, such as a disease, the microbes that reside in your gut can be disrupted. This will be different from the microbe community that was present when your body was healthy. This is termed as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis can be caused by change in eating habits, bowel movements and even medications taken when one is ill. However, it is to note that whether these changes in the microbiota are helpful or not is still under research. Some of the most common gut related disorders you would have come across are constipation, indigestion and diarrhea. In addition, conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, Celiac disease, lactose intolerance and colitis are also gut related.
What can i do to maintain a healthy gut ?
The following tips can be incorporated into your daily life to ensure the gut microbes are functioning well in order to support your body to function optimally;
Diverse diet:
A large and diverse community of microbes resides in our gut. So, to support these microbes, our diet needs to be equally varied. Our food serves as substrates for these microbes to thrive. It is clear that the diversity of our diet determines the diversity and richness of the gut microbiota. The increasing number of fad diets is also an issue of concern as it encourages elimination of food groups, which in turn affect the diversity of the gut microbiota.
Fiber intake and polyphenols also play key role in shaping the microbiome. Low intake of fiber paired with high fat and sugar intake may reduce certain microbe groups in the gut. Polyphenols are found in foods like tea, chocolate, spice, seasonings, herbs and even fruits and vegetables. Interactions between polyphenols and the gut microbes can also impact health.
What can you do ?

Ensure your diet is diverse by varying the foods you eat on a daily basis. Consume fiber rich food such as whole grains, lentils/legumes, fruits and vegetables. Aim for at least 25-30g of fiber a day. It is important to note that fruits and vegetable are rich in polyphenols thus are able to provide much additional benefits.
Fermented Foods
Fermentation is a natural process by which bacteria break down substances into simpler forms. Examples of fermented food are kimchi, yoghurt and kefir among several others. These are commonly termed as ‘probiotics’ since they contain live cultures of microorganisms. While the research on probiotics is still ongoing, they do seem to show promising effects on enriching the existing gut flora.

Stress

This is something that affects each one of us on a day-to-day basis. While everyone knows that extreme stress is unhealthy, we never expect stress to also affect the diversity of microbes in our gut. Hence, get enough sleep and limit your involvement in anxiety inducing environment as much as possible to avoid disrupting your gut microbiota and maintain a healthy body.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gut health is a growing area of research. While there are still a number of questions left unanswered, the field seems vast and promising. It is clear that the gut plays an important role in several aspects of human health. Thus, it is necessary for us to understand this and nourish the gut by practicing a healthy lifestyle.
References: