N-acetylcysteine, also known as Acetylcysteine, NAC or N-acetyl-cysteine, is a derivative of an amino acid called cysteine which is important in the production of glutathione, a potent antioxidant in human body.
Benefits of N-acetylcysteine
- Antioxidative function
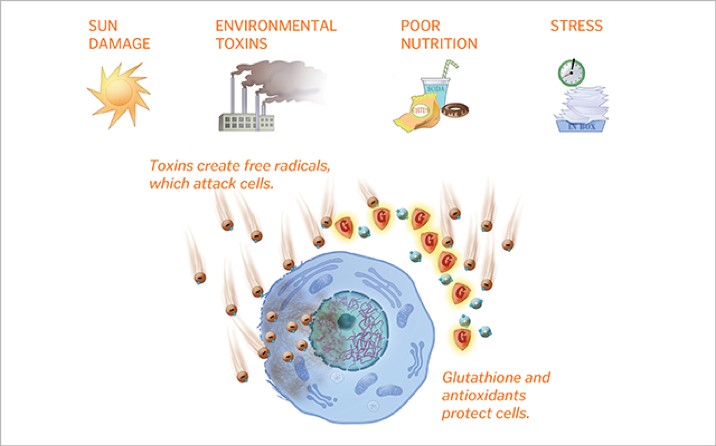
When consumed, N-acetylcysteine gets converted into L-cysteine, an amino acid that is the direct precursor to glutathione in human body. Glutathione is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals and thus protect your body cells and tissues from oxidative damage.1 Therefore, N-acetylcysteine acts as an antioxidant by replenishing the glutathione pool in body cells that becomes depleted with increased level of inflammation and oxidative stress in human body.2 This antioxidant property can help improve illnesses caused by oxidative stress, such as heart disease and infertility as well as help maintaining healthy function of immune system.3, 4, 5
2. Liver-protective function
N-acetylcysteine has been used for long as the mainstay treatment and antidote for paracetamol overdose to prevent or reduce liver damage.6 When given intravenously within 8 hours after the ingestion of paracetamol, the treatment is highly effective.6 N-acetylcysteine is also found to improve liver function in patients with non-paracetamol induced liver failure and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease thanks to its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effect.7, 8
3. Helps relieve symptoms of respiratory condition
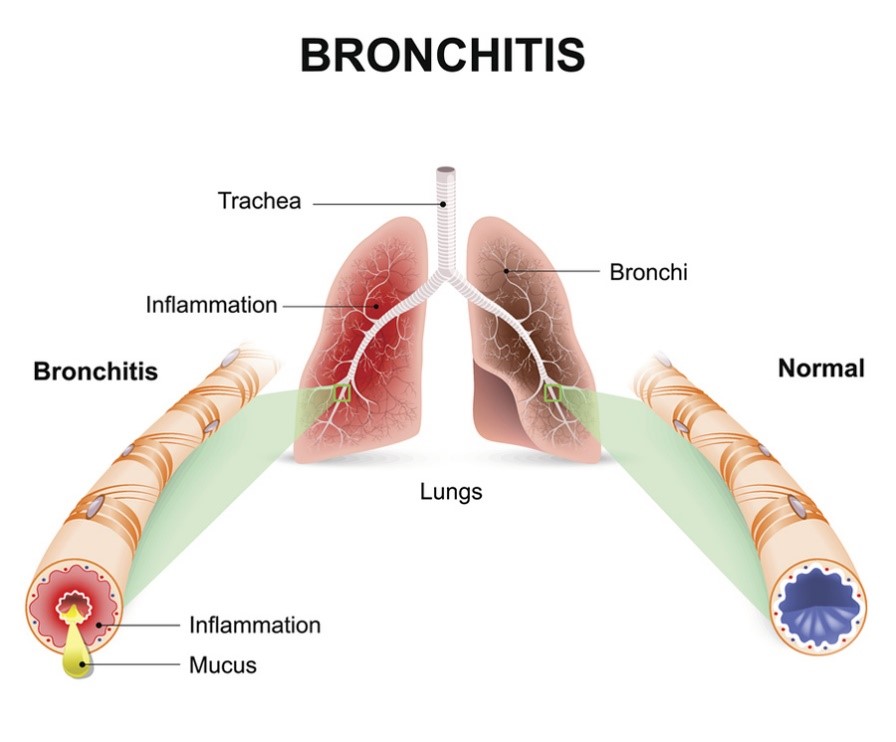
N-acetylcysteine is also commonly used to reduce phlegm in respiratory system. It achieves this effect by acting as mucolytic agent that reduces mucus viscosity and as a muco-regulatory agent which reduces airway mucus secretion.2 These effects, along with the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of N-acetylcysteine helps to improve breathing and lung function in lung disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis and many others.2, 9
4. Kidney-protective function
N-acetylcysteine has been speculated to be able to slow down the progress of chronic kidney disease by reducing serum creatinine and improving the structure of some of the cells in kidneys.10, 11
5. May improve mental health condition and substance use disorder
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in the use of N-acetylcysteine in helping to manage mental health conditions and substance use disorder. N-acetylcysteine has been discovered to be able to regulate the level of glutamate, an important neurotransmitter in human brain. 12 While glutamate is needed for normal brain activity, excess glutamate in brain has been found to be associated with mental illnesses such as schizophrenia or depression. 13, 14 When used in patient with substance use disorders, especially to treat young individuals addicted to cocaine and cannabis, N-acetylcysteine is effective in reducing the craving for the substances and can help abstinent individuals to prevent relapsing.13 There are also promising evidence for the use of N-acetylcysteine in treating obsessive-compulsive disorders and mood disorders, but better designed studies are required to further investigate its clinical effectiveness. 13
6. May improve fertility
N-acetylcysteine has been yielding positive results in studies that look into fertility improvement in recent years. It was found that N-acetylcysteine can be helpful in polycystic ovarian syndrome(PCOS)-related and unexplained female infertility, especially in women with high BMI, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress15 N-acetylcysteine is also discovered to have ovulation induction properties and thus can be an effective adjuvant to improves pregnancy rate in patients receiving intrauterine insemination.16 However, more well-controlled studies still need to be done to further confirm and establish the findings.

Risks and side effects of N-acetylcysteine
N-acetylcysteine on its own has very good tolerability and safety profile even at high dose.8, 13, 14 The most common side effects that are associated with it are mainly gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, gastric reflux, bloating. 14, 17
However, N-acetylcysteine can potentiate the vasodilation effect of Nitroglycerin, an antianginal medication which can lead to higher incidence of side effects such as headache and severe hypotension.18, 19
People who are taking blood thinning medication, have bleeding disorders or for those who are about to undergo major surgery also need to be cautious with the use of N-acetylcysteine because N-acetylcysteine has anticoagulant and platelet-inhibiting properties, thus can increase bleeding risk.20
References
- Ershad M, Naji A, Vearrie D. National Center for Biotechnology Information [Internet]. N Acetylcysteine. National Library of Medicine; 2023 [cited 2023Apr22]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537183/
- Sadowska AM. N-Acetylcysteine mucolysis in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease. 2012;6(3):127-135.
- Shackebaei D, King N, Shukla B, Suleiman MS. Mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective effect of L-cysteine. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005;277(1-2):27-31.
- Adeoye O, Olawumi J, Opeyemi A, Christiania O. Review on the role of glutathione on oxidative stress and infertility. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2018;22(1):61-66.
- Dröge W, Breitkreutz R. Glutathione and immune function. Proc Nutr Soc. 2000;59(4):595-600.
- Daly, F. F., Fountain, J. S., Murray, L., Graudins, A., & Buckley, N. A. (2008). Guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand-explanation and elaboration. Medical journal of Australia, 188(5), 296.
- Dludla PV, Nkambule BB, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, et al. N-Acetyl Cysteine Targets Hepatic Lipid Accumulation to Curb Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in NAFLD: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Literature. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(12):1283. Published 2020 Dec 16.
- Nabi T, Nabi S, Rafiq N, Shah A. Role of N-acetylcysteine treatment in non-acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: A prospective study. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(3):169-175.
- Cazzola M, Calzetta L, Page C, et al. Influence of N-acetylcysteine on chronic bronchitis or COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24(137):451-461.
- Tian N, Rose R, Jordan S, Dwyer TM, Hughson MD, Manning RD Jr. N-acetylcysteine improves renal dysfunction, ameliorates kidney damage and decreases blood pressure in salt-sensitive hypertension. J Hypertens. 2006;24:2263–2270.
- Ye M, Lin W, Zheng J, Lin S. N-acetylcysteine for chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(4):2472-2485.
- Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, et al., editors. Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2001. Glutamate. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10807/
- McQueen G, Lally J, Collier T, et al. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on brain glutamate levels and resting perfusion in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(10):3045-3054. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-4997-2
- Onaolapo AY, Onaolapo OJ. Glutamate and depression: Reflecting a deepening knowledge of the gut and brain effects of a ubiquitous molecule. World J Psychiatry. 2021;11(7):297-315.
- Devi N, Boya C, Chhabra M, Bansal D. N-acetyl-cysteine as adjuvant therapy in female infertility: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;32(5):899-910.
- Bedaiwy, M.A., RezkH. Al Inany, A. and Falcone, T. (2004) “N-acetyl Cystein improves pregnancy rate in long standing unexplained infertility: A novel mechanism of ovulation induction,” Fertility and Sterility, 82.
- Calverley P, Rogliani P, Papi A. Safety of N-Acetylcysteine at High Doses in Chronic Respiratory Diseases: A Review. Drug Saf. 2021;44(3):273-290.
- Horowitz JD, Henry CA, Syrjanen ML, et al. Nitroglycerine/N-acetylcysteine in the management of unstable angina pectoris. Eur Heart J. 1988;9 Suppl A:95-100.
- Ardissino D, Merlini PA, Savonitto S, et al. Effect of transdermal nitroglycerin or N-acetylcysteine, or both, in the long-term treatment of unstable angina pectoris. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;29(5):941-947.
- Niemi TT, Munsterhjelm E, Pöyhiä R, Hynninen MS, Salmenperä MT. The effect of N-acetylcysteine on blood coagulation and platelet function in patients undergoing open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17(1):29-34.























-260x200.jpg)
.jpg)




























-260x200.jpg)
.jpg)
/tuberculosis-risk-factors-causes-and-prevention-722x406.jpg)
/65590790_344571899553456_4477774208062980096_n.jpg)
















/image.png)


-260x200.jpg)
.jpg)