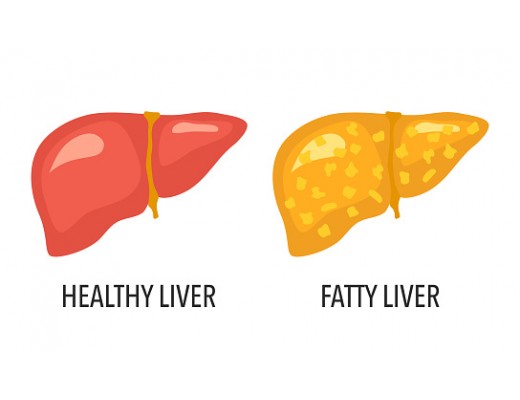
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a type of fatty liver disease that is not related to heavy alcohol use.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease is another type of fatty liver disease which is due to heavy alcohol use. The harmful substances which are generated during the alcohol breaking process may accumulate and damage liver cells. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease.
According to researchers, the cause of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is unknown, but this condition is more common in people who:
- Have type 2 diabetes
- Obesity with a high level of belly fat
- Are Hispanic or Asian
- Are middle aged or older
- Have high levels of fats in blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides
- Have high blood pressure
- Have rapid weight loss
- Have certain metabolic disorders, including metabolic syndrome
- Take certain drugs, such as corticosteroids and some cancer drugs
- Have certain infections, such as hepatitis C
- Have been exposed to some toxins
Alcoholic fatty liver disease only happens in people who are heavy drinkers, especially those who have been drinking for a long period of time.
SYMPTOMS
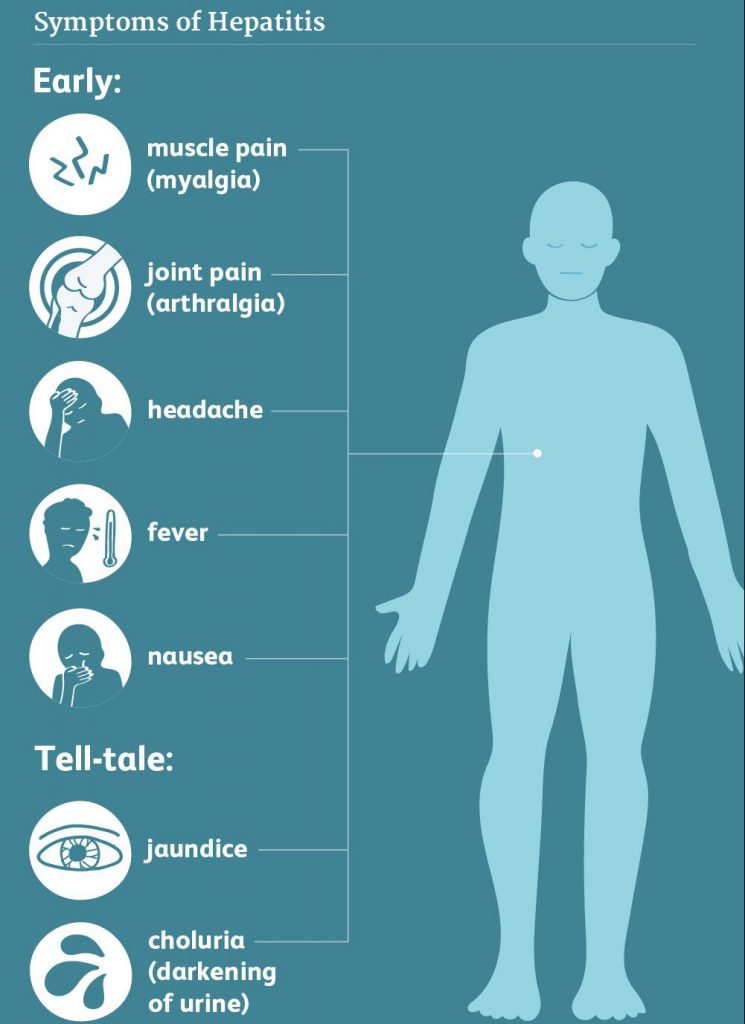
 Fatty liver disease is usually a silent disease with few or no symptoms until the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
Fatty liver disease is usually a silent disease with few or no symptoms until the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver. If you do have symptoms, they may include:- Abdominal pain or a feeling of fullness in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Nausea or weight loss
- Jaundice
- Swollen abdomen and legs (oedema)
- Tiredness and weakness
HOW IS FATTY LIVER DISEASE DIAGNOSED?
Laboratory abnormalities are often the only sign of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The most common abnormal laboratory test results are elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST). There are other methods to diagnose fatty liver disease, doctor may order:
- Ultrasound or CT scan to get a picture of the liver
- Liver biopsy to determine how far advanced liver disease has progressed
TREATMENT OF FATTY LIVER DISEASE
There is no medication specifically for fatty liver disease. Instead, doctors focus on helping the patient to control factors that contribute to the condition. Treatment includes:
- Avoiding alcohol for alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Losing weight for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Avoiding certain medicine that may cause NAFLD
- Taking medications to control diabetes, cholesterol and triglycerides
- Taking vitamin E and thiazolidinediones (drugs used to treat diabetes) in specific instances, but more studies are needed to support this.
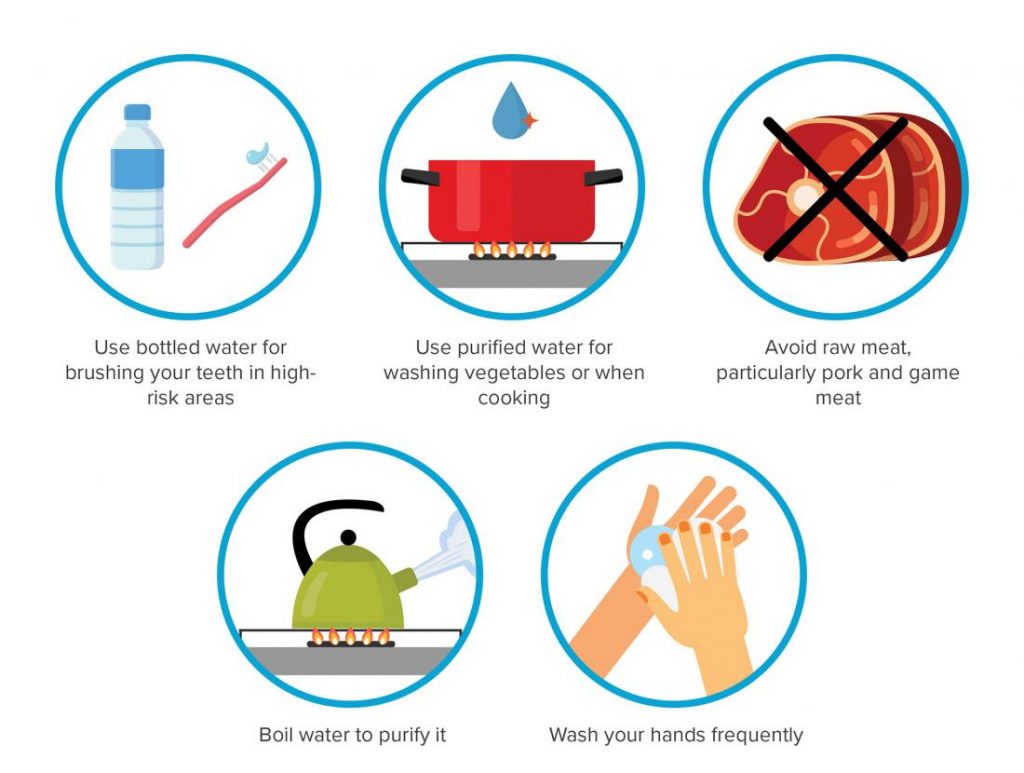
PREVENTION OF FATTY LIVER DISEASE
The best way to avoid fatty liver disease is to do the things that maintain overall health:
- Stay at a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly
- Limit or reduce alcohol consumption
- Take medication as prescribed
SUPPLEMENTS
Dandelion
Dandelion root contains high amounts of a substance called kynurenic acid, which is an amino acid that is the key for bile production. Researchers found that dandelion is amongst a group of healing herbs that can be highly beneficial for the gallbladder that can improve bile flow.
Dandelion also supports the liver by providing first-layer support for blood detoxification. It’s a great preventative for jaundice, gentle support for those who have hepatitis, and can also help with anaemia since it can encourage iron absorption. Another way that dandelion cleanses blood is by working with pancreas to remove excess sugars. So, dandelion is not only beneficial for liver detoxification, it can balance blood glucose level as well.
Flavonoids in dandelion promote increased urination, which can assist the liver in cleansing toxins out of the body at a more rapid rate.
Dandelion helps the liver to break down and absorb minerals. This is due to dandelion is a great source of vitamin A, B, C, E, K and key minerals, including calcium and potassium. Vitamin C is an important liver helper because it can assist in the breakdown of key minerals like iron.
Milk thistle
Milk thistle is an anti-fibrotic, which means it protects against tissue scarring. Thus, milk thistle can be used to combat liver damage and inflammation caused by acetaminophen, alcohol, chemotherapy and carcinogens.
Milk thistle has the powder to stimulate healing in the liver and protect it from future damage.
When the liver become too overloaded with toxins like heavy metals and pollutants, milk thistle supports the liver’s detoxification process. Milk thistle helps the liver effectively purify the blood, remove harmful substances from the body, produce hormones, and perform countless other essential responsibilities.
Artichoke
Contains a compound called luteolin, which is a potent antioxidant that prevents the synthesis of cholesterol.
The metabolism of cholesterol can be increased by consuming artichoke extract. Thus, it encourages the cholesterol breakdown and elimination. The overall effect is reducing levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and increases levels of good cholesterol (HDL) in the body.
REFERENCE
- Topics, H., 2022. Fatty Liver Disease | MedlinePlus. [online] Medlineplus.gov. Available at: <https://medlineplus.gov/fattyliverdisease.html> [Accessed 11 January 2022].
- Cleveland Clinic. 2022. Fatty Liver Disease: Risk Factors, Symptoms, Types & Prevention. [online] Available at: <https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15831-fatty-liver-disease> [Accessed 11 January 2022].
- Panahi Y, Kianpour P, Mohtashami R, Atkin SL, Butler AE, Jafari R, Badeli R, Sahebkar A. Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot double-blind randomized controlled trial. Phytother Res. 2018 Jul;32(7):1382-1387. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6073. Epub 2018 Mar 9. PMID: 29520889.
- Wirngo, F. E., Lambert, M. N., & Jeppesen, P. B. (2016). The Physiological Effects of Dandelion (Taraxacum Officinale) in Type 2 Diabetes. The review of diabetic studies : RDS, 13(2-3), 113–131. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2016.13.113
- Jacobs BP, Dennehy C, Ramirez G, Sapp J, Lawrence VA. Milk thistle for the treatment of liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2002 Oct 15;113(6):506-15. doi: 10.1016/s0002-93