STRETCH MARK
What exactly is a stretch mark?
A stretch mark is a type of scar that develops when our skin stretches or shrinks quickly. The abrupt change causes the collagen and elastin, which support our skin, to rupture. As the skin heals, stretch marks may appear. (1)
They’re common during puberty or pregnancy, in which they usually form during the last trimester. (2) The indented streaks (stretch marks) normally appear on the abdomen, breasts, hips, buttocks, thighs or other places on the body.(3) Stretch marks may also be influenced by the hormonal changes associated with puberty, pregnancy, bodybuilding, or hormone replacement therapy.(2)
Over time stretch marks may diminish, but will not disappear completely.(2) They aren’t painful or harmful, but some people don’t like the way they make their skin look.
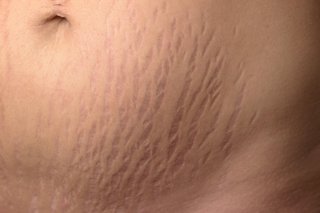
How stretch mark looks like?
Stretch marks don’t all look alike. They vary depending on how long you’ve had them, what caused them, where they are on your body and the type of skin you have.(3)
When stretch marks first appear, they tend to be red, purple, pink, reddish-brown, or dark brown, depending on your skin color. Early stretch marks may feel slightly raised and can be itchy.
In time, the color fades and the narrow bands sink beneath your skin. If you run your finger over a mature stretch mark, you often feel a slight depression.(1)


Who are more prone to getting stretch marks?
Anyone can develop stretch marks, but some factors increase your likelihood of getting them, including:
- Being female
- Having a personal or family history of stretch marks
- Being pregnant, especially if you’re young
- Rapid growth in adolescence
- Rapidly gaining or losing weight
- Using corticosteroids
- Having breast enlargement surgery
- Exercising and using anabolic steroids
- Having a genetic disorder such as Cushing’s syndrome or Marfan syndrome(3)
How to treat stretch marks?
Stretch marks are harmless and often fade over time. Treatment can make them fade, but they may never completely disappear.
The following treatments are among those available to help improve the appearance and texture of stretch marks. None has been proved to be more consistently successful than the others.
- Retinoid cream. Derived from vitamin A, retinoids — such as tretinoin (Retin-A, Renova, Avita) — that you apply to your skin may improve the appearance of stretch marks less than a few months old. Tretinoin, when it works, helps to rebuild a protein in the skin called collagen, making the stretch marks look more like your normal skin. Tretinoin can irritate your skin.
If you’re pregnant or nursing, talk with your doctor about other treatment options, because possible side effects of retinoid cream may affect the baby. - Light and laser therapies. A variety of light and laser therapies are available that might stimulate growth of collagen or promote elasticity. Your doctor can help you determine which technique is appropriate for you.
- Microneedling. This type of treatment involves a hand-held device with tiny needles that stimulate collagen growth. This technique has less risk of pigmentation changes than does laser therapy so is the preferred initial approach for people with darker skin.(3)
- Stretch mark creams, lotions, and gels. Researchers have studied many of the creams, lotions, and gels sold to treat stretch marks. While no one product seems to help all of the time — and some don’t seem to help at all — researchers have discovered some helpful hacks.
If you want to try one of these creams, lotions, or gels to fade stretch marks, be sure to use the product on early stretch marks. Treatment seems to have little effect on mature stretch marks. You should massage the product into your stretch marks. Taking time to massage the product gently into your skin may make it more effective. Applying the product every day for weeks may also increase effectiveness of the products. If you see results, they take weeks to appear.(1)
Work with your doctor to choose the most appropriate treatment or combination of treatments for you. Factors to consider include:
- How long you’ve had the stretch marks
- Your skin type
- Convenience, as some therapies require repeated doctor visits
- Cost
- Your expectations
How to prevent formation of a stretch mark?
Collagen and elastin are proteins in the skin that contribute to the skin’s strength, resilience, flexibility, and help skin that has been stretched to recover to its original state. Boosting the production of collagen and elastin helps prevent stretch marks from occurring.Stretch marks can also derive from nutritional deficiencies. Consuming foods that contribute to the skin’s health, such as zinc-rich foods, foods high in vitamin A, C, D, and protein rich foods, can help suppress stretch marks. (4)
References
- Stretch marks: Why they appear and how to get rid of them. (n.d.). https://www.aad.org/public/cosmetic/scars-stretch-marks/stretch-marks-why-appear
- Wikipedia contributors. (2022, December 22). Stretch marks. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stretch_marks
- Stretch marks – Symptoms and causes. (2022, August 23). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stretch-marks/symptoms-causes/syc-20351139
- Skin: Layers, Structure and Function. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/10978-skin