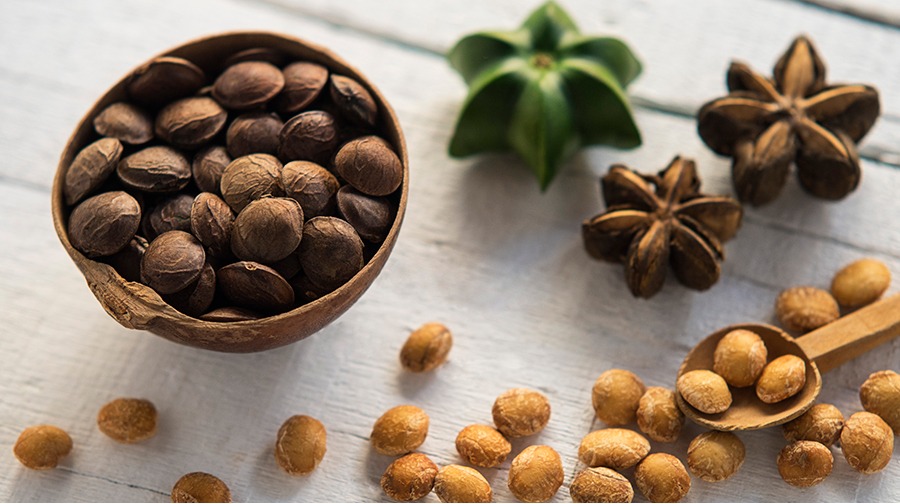
SACHA INCHI OIL: NUTRITIONAL CONTENT & ITS HEALTH BENEFIT

According to National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS 2019), about 1.7 million individuals in Malaysia are at risk of suffering from 3Hs, namely hypertension, hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol) and hyperglycemia (diabetes) which leads to cardiovascular disease. It is well known that cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in Malaysia.
Plukenetia volubilis L. (family Euphorbiaceae), commonly known as Sacha Inchi, Inca peanut or mountain peanut has been adopted as a food source due to its high nutritional value and potential benefits for human health. Sacha Inchi is used as a traditional remedy and in recent years has been introduced to cosmetics and dietary supplementation markets successfully.
Content of Sacha Inchi
Medicinal applications of Sacha Inchi have been discussed for a variety of diseases. Besides its cholesterol and blood pressure lowering properties, it is presumed that Sacha Inchi may promotes health improvements in diabetic, arthritis, cancers (breast cancer, prostate carcinoma) and in certain cases of psychological disorders patients. Due to its recognized high content of essential fatty acids, phenolic compounds and vitamin E, Sacha Inchi provides antioxidant properties, hypolipidemic, immunomodulation and emollient activity, as well as capacity to remove heavy metals from aqueous solutions.
Sacha inchi has been known to be rich in unsaturated fatty acids. Its seed contains:
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids like α-linolenic (ALA) and linoleic (LA), bases of ω-3 and -6, respectively, γ- and δ-tocopherols,
- Natural forms of vitamin E, known for its antioxidant activity and antitumor potential.
Essential fatty acids in the form of omega 3 and omega 6 contained in sacha inchi oil are 50.5% and 34.1% respectively, while the protein content in Sacha Inchi is 22-30%. These biomolecules are involved in immune functions, where it helps in mediating inflammatory response. Intake of omega-3 fatty acids from other sources is widely used to lower high blood triglyceride levels which positively influence blood flow and blood clotting. In this context, Sacha Inchi oil has been assumed to be an alternative to fish oil.
Studies on Sacha Inchi
Gonzales et al. conducted a study for four months on 15 males and 15 females without the history of hyperlipidaemia or any other disease likely to affect lipid metabolism showed that the permanent consumption of sacha inchi oil for four consecutive months showed 10 % increase in plasma HDL level. Other study also stated that consumption of 50 g of sacha inchi can significantly lower triglyceride levels. Although sacha inchi oil may have an unpleasant taste, it is believed that over time it can be accepted by consumers. Commercial sacha inchi oil is classified as extra virgin oil or virgin oil and has low oxidative stability thus should not be consumed hot.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids of Sacha Inchi is the main component that contributed to its beneficial function in variety of processes such as regulation of the inflammatory immune response, blood pressure, reduction of triglyceride levels in the circulation, prevention of neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorder, maintenance of memory and visual function. Supplementation of yoghurt with sacha inchi seeds has been studied recently, revealing an increase of the levels of ALA and LA of 25- and 50-fold respectively, from an average PUFA content of 3.60 to 81.51% in the modified product compared to the control.
It is considered that fatty acids with higher fraction of PUFA in sacha inchi are beneficial to human health due to their antiatherogenic, antithrombogenic and hypocholesterolemic effects, besides having a high nutritional value.
Sources of sacha inci
Sources of sacha inchi can be varies in these modern days. Various brands has marketed sacha inchi in form of oil and softgels. Some people would simply enjoy sacha inchi by roasting the seed or mix with other nuts for snacking.



References
- Cárdenas DM, Gómez Rave LJ, Soto JA. Biological Activity of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis Linneo) and Potential Uses in Human Health: A Review. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;59(3):253-266.
- Gonzales GF, Gonzales C. A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study on acceptability, safety and efficacy of oral administration of sacha inchi oil (Plukenetia volubilis L.) in adult human subjects. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;65: 168–76.
- Hanssen, H.-P. and Schmitz-Hübsch, M. (2011) Nuts and Seeds in Health and Disease Prevention, Chapter 117 – Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Nut Oil and Its Therapeutic and Nutritional Uses. Academic Press. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-375688-6.10117-3 (Accessed: April 14, 2023).