Hepatitis
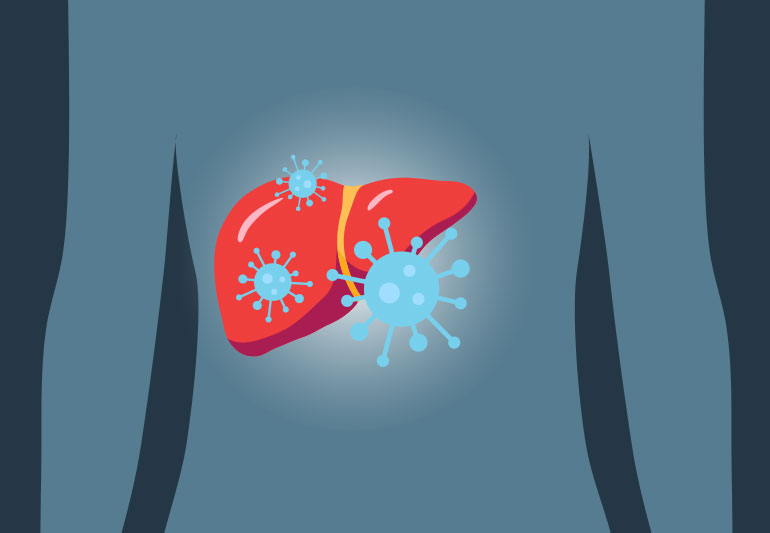
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that is caused by a variety of infectious viruses and non-infectious agents such as drugs, toxic agents, alcohol or certain genetic disorders leading to a range of health problems, some of which can be fatal. In some cases hepatitis is also the result of auto-immune reaction when the immune system mistakenly attacks the liver.
There are five main viral classifications of hepatitis, which are hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Different virus is responsible for each type of viral hepatitis. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 354 million people are currently living with hepatitis B and C.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is caused by hepatitis A virus (HAV). It can be spread through contaminated food and water. It is the easiest to be transmitted from one person to another person, especially among children, but is also the least likely to damage the liver. This type of infection is a short-term disease and is completely resolved within six months.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV). It can be spread through exposure to contaminated blood, needles, syringes or bodily fluids and from mother to baby. This is a chronic condition, in some cases it may lead to liver damage, liver cancer and cirrhosis in long term.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C is only transmitted through infected blood or from mother to baby during childbirth. It also can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer in long term.
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is only found in people who are also infected with hepatitis B.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease that results from exposure to the hepatitis E virus (HEV). Hepatitis E is usually spread via contact with food or water that was contaminated with an infected person’s stool.
Autoimmune Hepatitis
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver cells as harmful invaders and attacks them. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. It’s three times more common in women than in men.
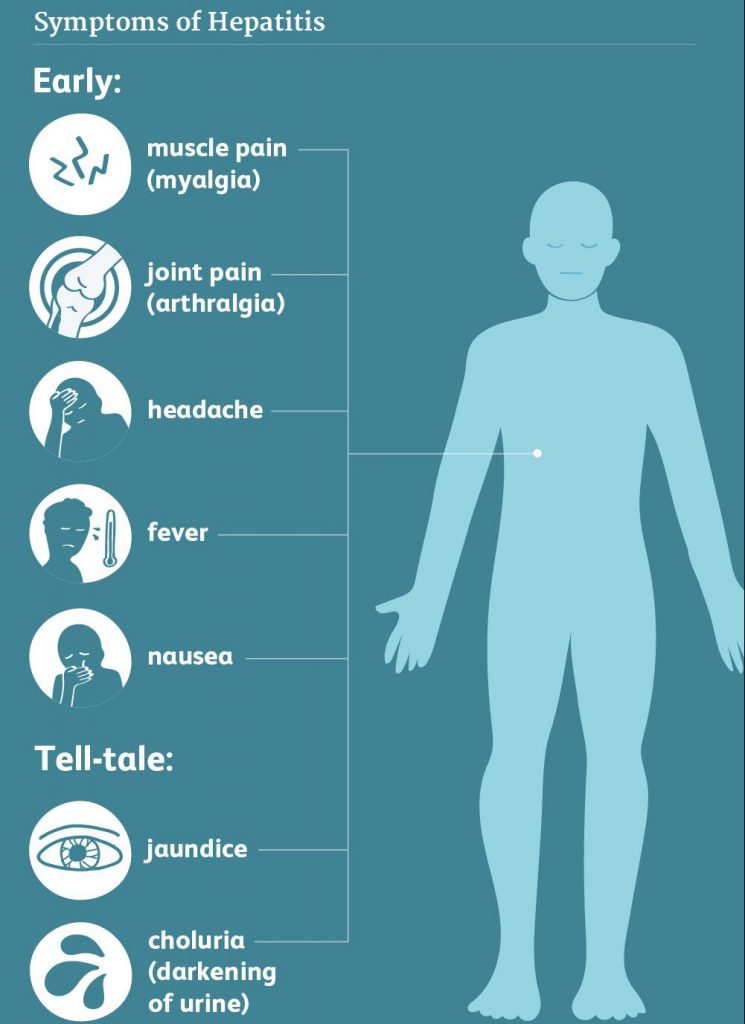
Symptoms
Fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice.
Causes
- Viral hepatitis can be caused by several viruses such as hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, and E.
- Alcoholic hepatitis can be caused by excess alcohol consumption.
- Toxic hepatitis can be caused by certain medicines, chemicals, poisons.
- Autoimmune happens when the immune system attacks liver cells, this condition is usually chronic.
Risk of Hepatitis
- Sharing needles or other objects that might be contaminated with hepatitis viruses
- Engaging in unsafe sexual contact, such as not using a condom during sex, having rough sex, or having multiple sexual partners
- Working around toxic chemicals. Examples of occupations routinely exposed to such chemicals include dry cleaners, painters, healthcare providers, or farm workers.
- Drinking untreated water or eating food that has not been safely or properly prepared (ex. unwashed produce)
- Drinking large quantities of alcohol over a long period of time
- Taking medications believed to be linked to hepatitis
- Not being vaccinated against viral hepatitis, specifically HAV and HBV
- Having an acute or chronic infection with one or more hepatitis viruses
- Having an autoimmune disorder
- Being born to a mother who is infected with a hepatitis virus, particularly hepatitis B
Diagnosis of Hepatitis
- Doctor will first take your medical history and symptoms.
- Physical exam will be done, which may or may not reveal a swollen, enlarged liver.
- Liver function tests, blood test (to check the presence of viral hepatitis) or ultrasound
- A liver biopsy to check for liver damage.
Treatment of Hepatitis
Treatment for hepatitis depends on which type of hepatitis you have and whether it is acute or chronic.
- Bed rest, refraining from alcohol, and taking medication to relieve symptoms.
- Most people who have hepatitis A and E get well on their own after a few weeks.
- Chronic Hepatitis B can be treated with antiviral medications
- Hepatitis C can be treated with a combination of antiviral drugs.
- Liver transplant may be needed if patient’s chronic hepatitis may lead to liver failure or liver cancer.
Prevention of Hepatitis
Get vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B
Vaccination for hepatitis A is available and can help to prevent the contraction of HAV. The hepatitis A vaccine is a series of two doses and most children will be vaccinated at age 12 to 23 months. This vaccination is also available for adults and can also include the hepatitis B vaccine.
The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccinations for all newborns. Doctors typically administer the series of three vaccines over the first 6 months of childhood.
The CDC also recommends the vaccine for all healthcare and medical personnel. Vaccination against hepatitis B can also prevent hepatitis D.
There are currently no vaccines that can prevent contraction of hepatitis C or E.
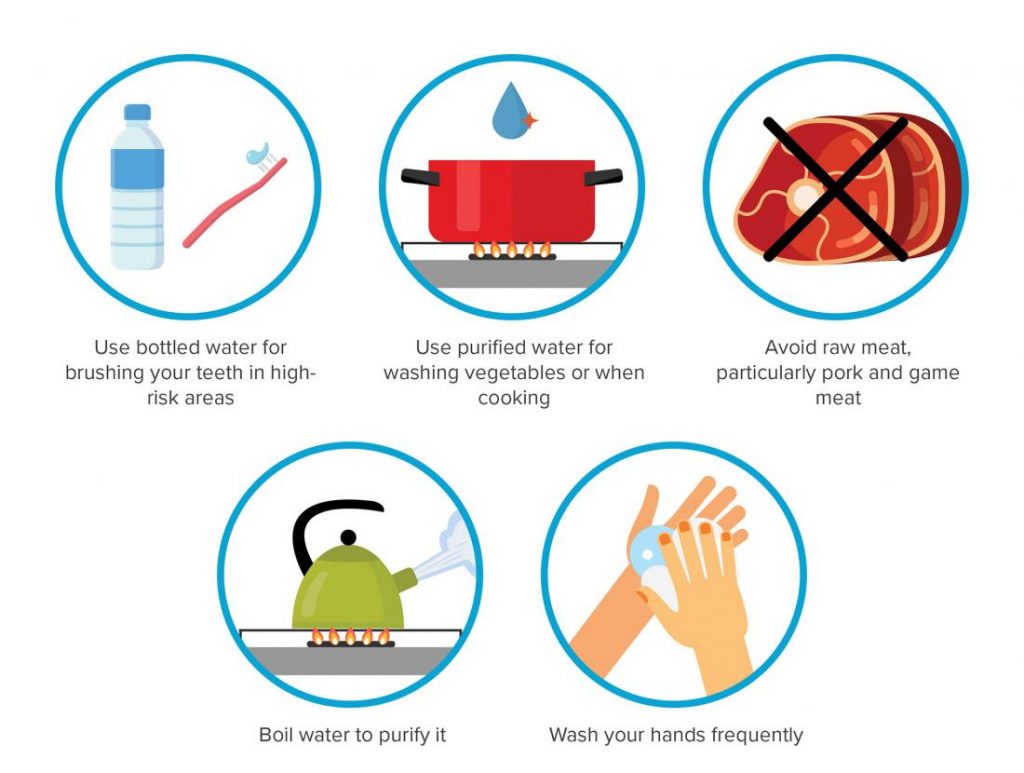
- Wash your hands after going to the bathroom and before handling food or eating.
- Use latex condoms, which may lower the risk of transmission.
- Don’t share drug needles.
- Don’t share personal items such as toothbrushes, razors and nail clippers with an infected person.
- Avoid raw or undercooked shellfish and oysters
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation. (Make sure to get vaccinated before your trips.)
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
References
1. World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis. Available at https://www.who.int/health-topics/hepatitis#tab=tab_1
2. Healthline. Hepatitis. Available at https://www.healthline.com/health/hepatitis
3. MedlinePlus. Hepatitis. Available at https://medlineplus.gov/hepatitis.html
4. Johns Hopkins medicine. Health. Hepatitis. Available at https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hepatitis
5. Verywell health. Causes and risk factors of hepatitis. Available at https://www.verywellhealth.com/hepatitis-causes-and-risk-factors-4689127#:~:text=Environmental%20risk%20factors%20associated%20with,blood%20infected%20with%20hepatitis%20viruses
6. Cleveland clinic. Viral hepatitis. Available at https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4245-hepatitis-viral-hepatitis-a-b–c#:~:text=There%20are%20many%20ways%20you,washing%20with%20soap%20and%20water