Sunblock or Sunscreen?

Types
Technically there is a huge difference between sunblock and sunscreen. Sunblock, as its name suggested, uses physical blockers like zinc or titanium oxide to guard the skin against UV rays. On the other hand, sunscreen uses active ingredients that readily absorb the sun’s rays. The active ingredients of sunscreens are more easily absorbed into the skin.
| SUNBLOCK / PHYSICAL SUNSCREEN | CHEMICAL SUNSCREEN | |
| Benefits | -Offers broad spectrum protection -Less likely to irritate the skin -Mostly non-comedogenic, hence less likely to clog the pores | -Thinner texture hence easier to spread evenly -Easily absorb into the skin, causing less residue |
| Drawbacks | -Need frequent reapplication as it disappears quickly -Some leave a white-hued residue on the skin -Thicker texture hence more effort is needed to rub in | -Need to apply at least 20 minutes before sun exposure to achieve the effect -May contain the chemical ingredients that can irritate the skin and eyes -More likely to clog pores, which can induce breakouts for those with oily skin |
Choose The Right One
1. Broad Spectrum Sunscreen
This type of sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are the one that contribute to skin cancer and premature aging while UVB rays can cause sunburn. Only products that pass a certain test can be labeled “broad spectrum.” Most of the products aren’t broad spectrum hence they can only protect against sunburn, not skin cancer or skin aging.
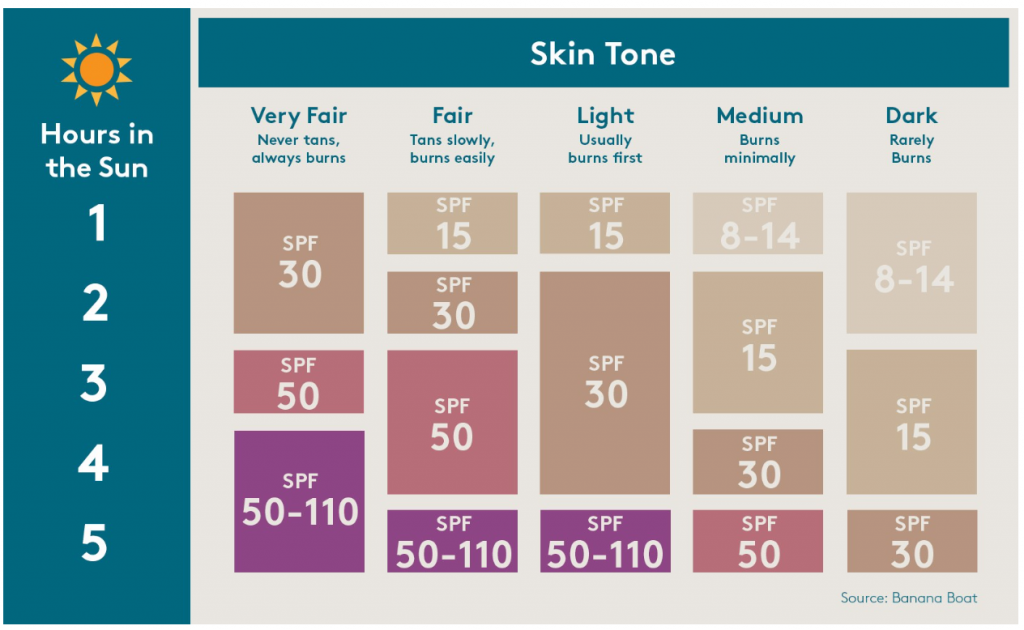
2. Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
SPF is a measure of how much UVB light can be filtered out by a sunscreen. The American Dermatology Association (ADA) recommends using an SPF of at least 30. SPF 15 blocks about 93 percent of UVB rays, while SPF 30 blocks about 97 percent of UVB rays.
3.Your Skin Type
For those who have dry skin should pick a sunscreen that doubles as a moisturizer.
For those who have oily and acne-prone skin, a water-based sunscreen instead of oil-based sunscreen is recommended.
On the other hand, for those with skin that is more sensitive and prone to irritation, they shall avoid products with alcohol, preservatives, fragrances, and oxybenzone.
The best sunscreen for kids should be at least SPF50. Choose sunscreens that are specifically made for kids as adult sunscreens can sometimes irritate their gentle skin. Babies need even stronger sun protection, as their skin is thinner and more. sensitive.
4.Level Of Sun Exposure
Duration of exposure to sunlight, the weather, and type of activities while being exposed to the sun are the factors that need to be taken into consideration. Typically, the strength of the sun is measured by the Ultraviolet (UV) Index, which ranges from 1 (low) to 11+ (extreme). These UV rays are the strongest from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., and when the UV Index is at 8 or above, our unprotected skin can burn in 15 minutes or less.
For instances,
– Outdoors: choose sunscreen with at least SPF 30 or higher if you are mostly outdoors for an extended period (two hours or more), depending on your skin color.
– Sports/swimming: choose a sweat-resistant or water-resistant sunscreen with at least SPF 30 or higher, depending on your skin color, and reapply every 40 to 60 minutes.
– Every day: choose sunscreen with at least SPF 15 on regular basis if you will be in the sun and shade.
5. Types of Formulation and Packing
Sunscreen formulation refers to how a sunscreen is formulated either an oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsion. It can be formulated in lotion, gel or cream thus it will give different textures and looks on an individual’s skin.
There are few common sunscreen formulations available on the market such as sunscreen sprays, sunscreen lotion and sunscreen stick. In general, all sunscreens have a shelf life of three years from the date of manufacture.
6. Water Resistance
There is a myth saying that “water resistant” means “waterproof.” No sunscreens are waterproof or “sweatproof,” you’ll need to reapply once you expose your skin to water with the product on, after a stipulated amount of time. Usually, reapplication of sunscreen at least every 2 hours is most favorable. If a product’s label makes claims of being water resistant, it must indicate whether it lasts for 40 minutes or 80 minutes while swimming or sweating.
Tips for sun-safe
- Wear clothing and wide-brimmed hat to protect the skin as much as possible. Pair up with sunglasses that block at least 99 percent of UV light to protect your eyes
- Look for shade. Limit direct exposure to the sun, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are the strongest.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps.
- Always remember to apply sunscreen or sunblock 15 minutes before you go outdoor to maximize the benefit of sunscreen.
References
- How to choose the best sunscreen, according to these dermatologists. [Internet]. Better By Today. 2019 [cited 5th June 2022]. Available from: https://www.nbcnews.com/better/lifestyle/how-choose-best-sunscreen-according-these-dermatologists-ncna1002451?featureFlag=true#anchor-NextconsidertheSunProtectionFactorSPF
- How to Choose Sunscreen. [Internet]. StyleCraze. 2022 [cited 5th June 2022]. Available from https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/things-to-consider-when-choosing-a-sunscreen/
- How Does Sunscreen Work to Protect Your Skin? [Internet]. Colorescience. 2018.[cited 5th June 2022]. Available from https://www.colorescience.com/blogs/learn/how-does-sunscreen-work-to-protect-your-skin
- Sunscreen: How to Help Protect Your Skin from the Sun. [Internet]. FDA. 2021. [cited 5th June 2022]. Available from https://www.fda.gov/drugs/understanding-over-counter-medicines/sunscreen-how-help-protect-your-skin-sun
- Choose the Right Sunscreen. [Internet]. cancer.org 2018. [cited 5th June 2022]. Available from https://www.cancer.org/latest-news/choose-the-right-sunscreen.html
- How To Choose Sunscreen To Suit Your Skin Type. [Internet]. Dermaster. 2021. [cited 5th June 2022]. Available from https://dermaster-thailand.com/en/resource/how-to-choose-sunscreen-to-suit-your-skin/