Erectile Dysfunction(ED)
.jpg)
Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough to have sexual intercourse. Erectile dysfunction is usually caused by low blood flow to the penis or problem with the nerves that control erections. Having trouble erecting for short period of time is not necessarily a cause for concern but it can cause stress, affect your self-confidence and contribute to relationship problems if it becomes an ongoing issue.
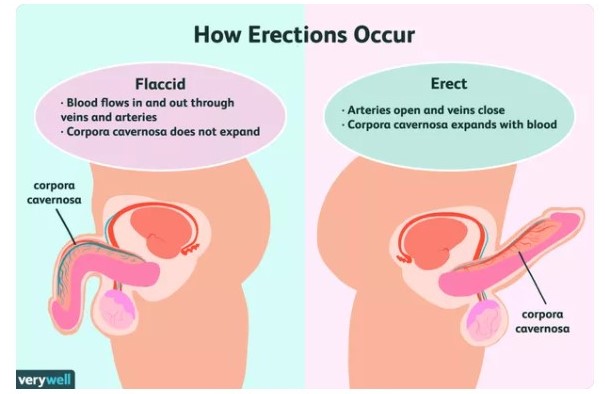
What are the symptoms of erectile dysfunction (ED)?
The symptoms include persistent:
- Trouble getting an erection
- Trouble keeping an erection
- Reduced sexual desire
What causes erectile dysfunction (ED)?
Problems getting or keeping an erection can be due to various risk factors, including:
- Vascular diseases (such as atherosclerosis which means hardening of arteries): These conditions narrow the blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis.
- Neurological disorders (such as multiple sclerosis which is a chronic disease affecting the brain and spinal cord): Nerves that send impulses to the penis can become damaged from stroke, diabetes, or other causes.
- Psychological states: These include stress, depression, lack of stimulus from the brain as well as performance anxiety.
- Trauma: An injury could contribute to symptoms of ED.
- Chronic illness, certain medications, and operations for the prostate, bladder, and colon cancer may also be contributing factors.

How is erectile dysfunction (ED) treated?
- Get More Exercise
Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and decreases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, all of which can have an impact on sexual function.
- Stop Smoking
Smoking affects circulation in ways that can inhibit blood flow to the penis and affect the ability to achieve or sustain an erection. Besides, smoking cessation has many other health benefits, such as reducing heart disease and diabetes which are the two major causes of ED.
- Eat Well
The risk of ED can be reduced in people who always eat diets that rich in whole-grain foods, vegetables, and fruits and low in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and sugary foods and drinks have a reduced risk of ED.
- Prescription Medications
The oral medications for erectile dysfunction enhance the effects of nitric oxide which is a natural chemical your body produces to relaxes muscles in the penis. This increases blood flow and lead to erection in response to sexual stimulation.
| Viagra (sildenafil) | May be effective within 30 to 60 minutes can last up to 12 hours |
| Cialis (tadalafil) | May be effective within 60 to 120 minutes and may last up to 36 hours |
| Levitra or Staxyn (vardenafil) | May be effective within 30 to 60 minutes and can last up to 10 hours |
| Stendra (avanafil) | May be effective within 15 to 30 minutes and can last up to 12 hours |
For Viagra, Levitra, and Stendra—eating a high-fat meal may delay the absorption of the drug, which will prolong the time for erection and diminish the drug’s overall effectiveness.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy
A healthcare provider may prescribe testosterone replacement therapy if a man is found to have a low testosterone level, along with other symptoms, such as low libido and ED. That said, testosterone deficiency is uncommonly the primary cause of ED. Before you take testosterone, your healthcare provider will have you tested to make sure that you do indeed have a deficiency.
- Reviewing Current Medications
It is very possible that one or more of current list of medications may be causing or contributing to your erectile dysfunction. Medications that classically cause erectile dysfunction as a side effect are antidepressants, especially selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as Zoloft (sertraline). Other potential medications linked to erectile dysfunction include certain blood pressure medications and pain medications.
- Pumps and Implants
A mechanical device may be worth trying if medications and other interventions don’t work.
One option is a vacuum pump, a plastic tube that is placed over the penis. When air is sucked out of the tube it creates pressure that causes blood to be forced into the penis. A ring can then be temporarily placed at the base of the penis to stop the blood from draining away too quickly.
A penile implant is another option. There are two types of penile implant. The first type is called a semi-rigid penis implant, it keeps the penis erect all the time, though it can be bent downward when you aren’t having sex. The other type is an inflatable two- or three-piece penis implant, it includes a pump that’s implanted in the scrotum and can be squeezed in order to make the penis erect.
- Natural Remedies
Research has found that certain natural remedies can improve ED to some extent. Here is a guide of herbs and supplements that may help improve the symptoms of erectile dysfunction:
| Studied in people, positive results, generally safe | ||
| Herb or supplement | Does it work? | Safety |
| DHEA | Some evidence shows that dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) increases libido in women and helps erectile dysfunction in men. | DHEA appears to be safe at low doses. It can cause acne. |
| L-arginine | Some evidence shows that taking high doses of L-arginine improves erectile dysfunction by stimulating blood vessels to open wider for improved blood flow | Side effects may include nausea, cramps and diarrhoea. However, it is not recommended to take L-arginine with sildenafil (Viagra). |
| Ginseng | One study of Panax ginseng has shown that it improves sexual function in men with erectile dysfunction. A cream preparation is used for premature ejaculation. | Panax ginseng contains many active ingredients. It appears to be safe if used on a short-term basis. Insomnia, headaches and vertigo are common side effects. |
| Propionyl-L-carnitine | Studies have shown that propionyl-L-carnitine if combined with Viagra might improve erectile function better than sildenafil alone. | Propionyl-L-carnitine is likely to be safe when used under medical supervision. |
References:
- Michael Bihari, MD (2021) Causes and Risk Factors of Erectile Dysfunction.
Available at: https://www.verywellhealth.com/erectile-dysfunction-causes-and-risk-factors-1124108 - Alana Biggers (2019) Everything You Need to Know About Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction#_noHeaderPrefixedContent - US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2019) Erectile Dysfunction.
Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/definition-facts - Borrelli F, et al(2018) Herbal dietary supplements for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Available at: doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0897-3. - U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2018) ‘All natural’ alternatives for erectile dysfunction: A risky proposition.
Available at: https://www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/ucm465024.htm.