WEIGHT MANAGEMENT

Body weight is one of many determinants of health. Maintaining a healthy body weight can lower your risks towards many weight-related diseases and health issues. However, each person’s healthy weight range will vary and depend on factors such as age, gender, genetics, body frame, existing medical history and lifestyle habits. So, weight management is a process of adopting long-term lifestyle modification to maintain a healthy body weight on the basis of these factors.
You may assess your body weight status via two simple physical examination methods:
Body mass index (BMI)
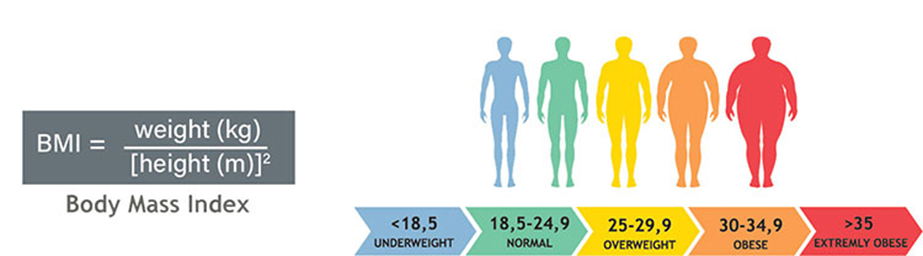
BMI is a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. A high BMI can indicate high body fatness, and a low BMI can indicate too low body fatness.
- If your BMI is less than 18.5, it falls within the underweight range.
- If your BMI is 18.5 to 24.9, it falls within the normal or healthy weight range.
- If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range.
- If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range.
Waist Circumference

Another way to estimate your potential disease risk is to measure your waist circumference. It is also a good estimate of visceral fat, the dangerous internal fat that coats the organ. Waist circumference measurement correlates well with abdominal fat content irrespective of the BMI. It is most useful in individuals who are in the normal and overweight categories of BMI. Your waistline may be telling you that you have a higher risk of developing obesity-related conditions if you are:
- A man whose waist circumference is more than 40 inches
- A non-pregnant woman whose waist circumference is more than 35 inches
Being too thin (underweight) or obese (overweight), both may impact your health condition. Maintaining a healthy weight is not only important for improving your physical appearance but is also beneficial for your overall well-being. Prioritizing weight management not only lowers the health risks but can also lead to an improved quality of life.
Underweight is a condition when energy intake is less than energy expenditure, it may lead to health risks such as malnutrition, decreased immune function, osteoporosis, infertility, developmental delays, and increased risk of surgical complications 2. A person may be underweight due to genetics, improper metabolism, lack of appetite, over-exercising, certain medicines, and underlying medical problems such as overactive thyroid, anorexia, etc 3.
Overweight and obesity are consequence of an energy imbalance where energy intake has exceeded energy expenditure over a considerable period of time, lead to abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. Obesity is one side of the double burden of malnutrition, and today more people are obese than underweight in every region. It once considered a problem only in high-income countries, overweight and obesity are now dramatically on the rise in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban settings. The World Health Organization (WHO) reported one in five Malaysian adults will be obese by 2025 4. Obese and overweight people are more prone to illnesses and conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, heart diseases, gall bladder diseases and osteoarthritis. Obesity may influence the risk of cancers of the colon, rectum, prostate, gall bladder, cervix, endometrium and ovary. Obesity also affects mobility, physical endurance and other functional measures. Obese people may also have low self-esteem 5.

Factors Weight Gain
Poor diet and overeating
Poor eating habits are probably the leading cause of obesity among all others. More often than not, people are likely to gain weight when they consume more calories than they burn through physical activity. Examples of unhealthy eating choices that directly lead to weight gain include:
- Eating more portions than your body needs
- Eating excessive amounts of processed or fast food
- Consuming beverages with too much sugar content
- Drinking too much alcohol 6
Physical inactivity
Another important factor is the lack of physical exercise. Nowadays, most people’s work desk jobs that consist of sitting and staring at a computer for long hours every day. When it comes to leisure activities, many of us prefer to lounge around and binge-watch or scroll endlessly on our phones instead of heading out to exercise. If you fail to incorporate exercise into your daily lives, the energy provided by the food you eat will only be stored by the body to become fat, which can lead to excessive weight gain 6.
Stress, emotional factors, and poor sleep
Some people eat more than usual when they are bored, angry, upset, or stressed. This “stress eating” are due to secretion of stress hormone called cortisol in our body. It increases appetite and may ramp up desire to eat fatty, salty or sugary “comfort foods” 7. Studies also have found that the less people sleep, the more likely they are to have overweight or obesity. This is partly because hormones that are released during sleep help control appetite and the body’s use of energy 8.
Health Conditions
On fairly rare occasions, obesity could be caused by certain health conditions. Examples of medical conditions that commonly contribute to weight gain include hormonal imbalance, hypothyroidism and Cushing’s syndrome. Other medical problems such as arthritis can hinder one from engaging in physical activity, which can ultimately result in weight gain as well. Certain medicines also may cause weight gain, including some corticosteroids, antidepressants, and seizure medicines 8.
Ways to Achieve Healthy Weight
Healthy eating

Healthy eating features a variety of healthy foods. Fad diets may promise fast results, but such diets limit your nutritional intake, can be unhealthy, and tend to fail in the long run. A healthy eating plan shall:
- Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products
- Include a variety of protein foods such as seafood, lean meats and poultry, eggs, legumes (beans and peas), soy products, nuts, and seeds.
- Is low in added sugars, sodium, saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Stay within your daily calorie needs 9.
Exercise regularly and stay physically active
Engaging in physical activity is one of the simplest ways to get rid of excess weight on your body. The more you exercise, the more calories your body burns off. On top of burning fat, exercising also increases your metabolism significantly 6. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommended regular exercise 60 minutes per day for children and 150 minutes per week for adults, to lower the risk or overweight and obesity 4.
Set smart weight goals
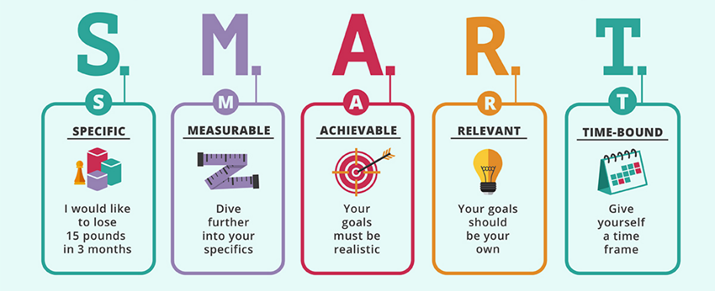
Losing or gaining weight does not happen overnight. A good and healthy weight loss or weight gain should adopt the concept of energy balance as its guiding principle. Setting a SMART goal should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and timely. For example, if your BMI is 23 kg/m2 and above, losing 10% to 15% of your current body weight over 6 months at a rate of 0.5 kg to 1 kg a week is a healthy target 10.
Last but not least, a heathy and successful weight management include regular monitoring of your progress and maintenance of healthy weight in the long term. Making lifestyle modifications goes beyond the physical aspects, this requires you to tap into your mental stamina as well. Believe it or not, your outlook or mindset can play an essential role in your weight management journey.
Reference:
- Assessing Your Weight. (2022, June 3). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/index.html
- Marcin, A. (2017, May 15). 6 Health Risks of Being Underweight. Healthline. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/underweight-health-risks
- Underweight | Office on Women’s Health. (n.d.). Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.womenshealth.gov/healthy-weight/underweight
- Obesity. (2020, February 21). Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1
- Surainee bt. Wahab. (2012, April 20). Weight Management. PORTAL MyHEALTH. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/index.html
- Homage. (2022, January 4). Weight Management Programmes by Doctors in Singapore. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.homage.sg/resources/weight-management/
- Harvard Health. (2021, February 15). Why stress causes people to overeat. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/why-stress-causes-people-to-overeat
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2012). What causes overweight and obesity? Retrieved September 10, 2012, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/overweight-and-obesity
- Physical Activity for a Healthy Weight. (2022, June 16). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/physical_activity/index.html
- HealthHub. (n.d.). Retrieved September 10, 2022, from https://www.healthhub.sg/live-healthy/410/Healthy%20Weight