What is Diabetes?
You may have heard that diabetes is a silent killer, because it takes away your life, parts by parts. The prevalence of diabetes has became worse as the year goes by as a recent survey from Health Ministry showed that nearly one in five Malaysian adults, or 18.3%, has diabetes.
Diabetes is a health disorder in when our body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin, resulting in a buildup of extra sugar in our bloodstream.
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a type of hormone released from the pancreas that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood by helping the glucose to move from the blood into the cells.
Types of Diabetes
| Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | |
| What is happening? | Caused by autoimmune disease when the pancreas produces too little or no insulin | Pancreas produces insulin, but the body doesn’t respond normally to the insulin produced. |
| Age of onset | Childhood | Adulthood |
| Risk factor | No known cause, and there is no way to reverse or cure it. Not associated with excess body weight, some affected patients might even be underweight. | Commonly associated with poor lifestyle and diet, such as excess body weight, age, physical inactivity, race and ethnicity, family history and poor control of blood lipid profile. |
| Management | Required insulin therapy | Can be managed by lifestyle modification such as diet and exercise if diagnosed early. Medication can be prescribed by doctor. |
| Cure and prevention | Cannot be prevented | Can be prevented by lifestyle changes |
Diabetes Diagnosis
Pancreas is a gland located behind the stomach in the upper left abdomen. Pancreas will release insulin as sugar metabolism. Insulin plays an important role in keeping blood glucose level within a healthy normal range. Thus, some tests can be conducted to check whether you are diabetic. Following tests are available at pharmacy:-
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C) measures your average blood glucose level for the past 3 months. It measures how much of glucose attached to your Hb (hemoglobin) as our Hb only lives for about 3 months. This test is shown to have higher sensitivity of identifying risk of diabetes. Reduction of HbA1C significantly reduces diabetes complications. HbA1C should always be less than 6.5%.
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) measures blood glucose level after fasting for at least 8 hours. It is usually done in the morning without breakfast; only plain water is allowed. Fasting glucose level should be below 5.6 mmol/L.
- Random Plasma Glucose (RPG) measures the blood glucose level at anytime of the day. RPG should be less than 8.0 mmol/L.
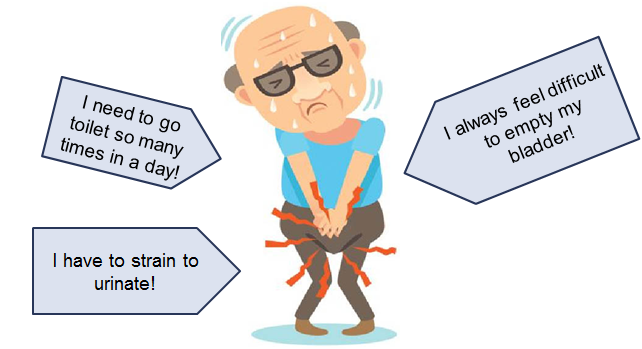
Symptoms of Diabetes
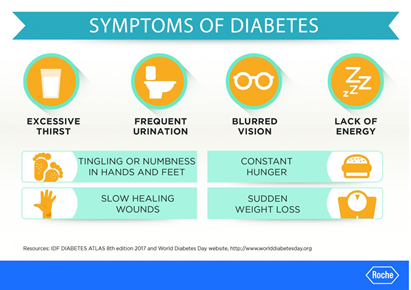
Sources: Accu-chek.co.uk/sign and symptoms of diabetes
The common term to remember is The 3 P’s of Diabetes, which is
- Increased hunger (Polyphagia) – The feeling of hunger that is not easily satisfied.
- Increased thirst (Polydipsia) – most likely as a result of frequent urination.
- Frequent urination (Polyuria) – result from increased renal activity as kidneys need to filter out excess sugar in the blood.
Furthermore, diabetes also comes with other symptoms such as tired/fatigue, nausea, numbness and tingling of hand and feet, blurred vision, sudden weight lost, sexual problem and slow healing of wound.
Complications of diabetes
Complications of diabetes are the most worrying part in diabetes as the symptoms will develop gradually. Over time, uncontrolled blood glucose level results in the higher risk to get the complications. Eventually, it may disable and even life threatening.
- Nerve Damage (Diabetic neuropathy) – High blood sugar can injure the wall of tiny blood capillaries that nourish your nerves throughout your body. It can cause pain, numbness, burning or tingling sensation, especially on your legs. When one nerve is damaged, it is gradually spread to multiple neurons. Thus cause alteration of functional organ in body can result in problem such as nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea. For men, glucose damage the nerve which blood supply to penis, thus cause erectile dysfunction.
- Kidney Damage (Diabetic Nephropathy)- Diabetes can damage your kidney due to kidney need to consistently wash away the glucose in your bloodstreams. The damaged kidney become leaky and let protein enter to your urine. It can progress to irreversible end-stage kidney diseases or kidney failure. This may require dialysis or kidney transplant on later stage.
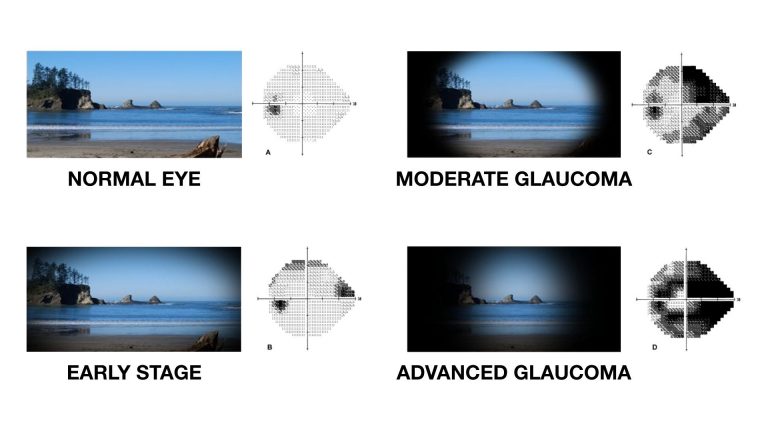
- Eye Damage (Diabetic Retinopathy)- Diabetes damage the small capillaries in your retina, cause it to break down (hemorrhage), which potentially cause vision loss or blindness. It also increases risk of developing other eyes problem such as glaucoma and cataracts.
- Cardiovascular disease – if you have diabetes, you are more risk to heart disease, including chest pain (angina), heart attack and narrowing of arteries (arteriosclerosis) and even stroke.
- Diabetic foot– Nerve damage to feet increases various foot complications. Infection from cuts and blister often occur due to poor wound healing. Diabetes may cause you more susceptible to skin problem, which will worsen the condition. Left untreated, this infection may require amputations.
Lifestyle Modification
- Low GI ( Glycemic Index) food– The amount and type of carbohydrate consumed will affect the blood glucose level after meals. We can plan a meal with low GI food. GI tells us a how quickly a food raise our blood glucose. GI is ranged from 0 to 100, tested by pure glucose. GI with less than 55 is considered low and it is useful to help manage glucose level. Some diabetic nutritional drink can be used as a meal replacement for diabetic individual. Other than that, good sources of carbohydrate include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes can be added. Increase fiber intake and whole grain food helps in increasing insulin sensitivity and thus overcome insulin resistance. You should also get good vitamins and minerals from healthy and balance diet.
- Artificial Sweetener– Diabetic individual should limit or avoid sugar sweetened beverages. It is a good start to swap sugary drink, energy drink, fruit juice into water, plain milk, tea and coffee. You may always try out low or zero-calories artificial sweetener as substitutes to control your blood glucose level.
- Cut down alcohol intake– Alcohol is high in calories that will spike up your glucose level. It should be limited to1 drink per day (women) and less than 2 drink per day (men).
- Eat less salt and processed food – Salt and processed food can increase risk of hypertension, which later leads to cardiovascular disease. Sodium intake should be less than 1 teaspoon per day. You can change your diet to omega-3 rich fatty acid food. EPA and DHA have beneficial effect on preventing heart disease.
- Quit smoking– Smoker are likely to develop diabetes compare to non-smoker. Nicotine replacement therapy can be considered to make it easier to quit. The faster you quit, the faster the body start to heal.
- Exercise regularly– being more physically active help to control your diabetes. When our muscles work, they take in glucose from the blood, liver and muscle. It improves cardiovascular risk, improve muscle strength, and contribute to weight loss.
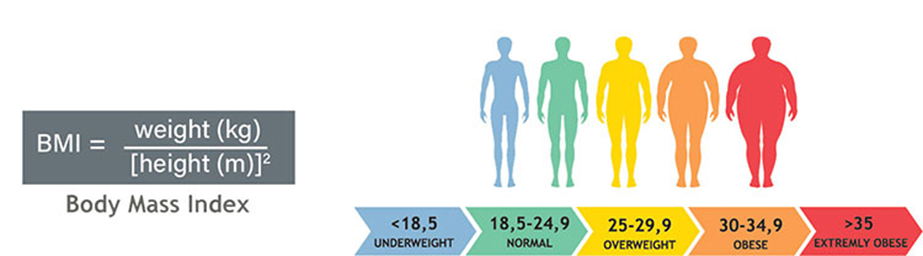
- Weight Management– You should be able to find out your Body Mass Index (BMI). Body Mass Index is a simple calculation using a person’s height and weight. The formula is BMI = kg/m2 where kg is a person’s weight in kilograms and m2 is their height in metres squared. A BMI of 25.0 or more is overweight, while the healthy range is 18.5 to 24.9. BMI applies to most adults 18-65 years. In addition to BMI, other physical measurements, such as body fat percentage, distribution of body fat and waist circumference, are important methods of assessing overweight and obesity. Modest weight loss of 10% over 6 months may improve glucose level responds.
- Foot care – People with diabetes are prone to have skin infections, including bacterial and fungal infection. Performing daily foot inspection and care is very important in avoiding serious foot complications. It is also necessary to perform regular checking of wound or infection that does not heal. With proper foot care, it is estimated that as half of the foot and leg amputation can be prevented.
References
- American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Understanding A1C: Diagnosis. https://www.diabetes.org/a1c/diagnosis
- Carbohydrates and the glycaemic index. (2020, March 16). Betterhealth. Retrieved July 24, 2021, from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/carbohydrates-and-the-glycaemic-index#bhc-content
- Diabetes Mellitus. (n.d.). MIMS. Retrieved July 24, 2021, from https://specialty.mims.com/diabetes%20mellitus/patient%20education
- Diabetes Signs. (2019, January 15). Diabetes.co.uk. Retrieved July 23, 2021, from https://www.diabetes.co.uk/The-big-three-diabetes-signs-and-symptoms.html
- Diabetes. (2020, October 30). Mayoclinic. Retrieved July 23, 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
- Dionardo, M. J. (2021, May 15). 6 Lifestyle Changes to Control Your Diabetes. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/diabetes-lifestyle-tips
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. (2020). Clinical practice guidelines: Management Of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (6th ed.). Retrieved from https://www.moh.gov.my/























-520x400.jpg)
.jpg)
/tuberculosis-risk-factors-causes-and-prevention-722x406.jpg)
/65590790_344571899553456_4477774208062980096_n.jpg)
















/image.png)


-520x400.jpg)
.jpg)




-520x400.jpg)
.jpg)
/the-dash-diet-1-638.jpg)
/low-sodium-diet-cover-adobe-1600x900-1-768x432.jpeg)
/noAlcoholSafe-481329705-650x450-650x428-1.jpg)
/Norway-reduces-sugar-consumption-768x432.jpg)